2021-06-15
How to create scroll view capable with dynamic content size.
Summary
This blog explains how to create scroll view even you don't know the inside content size. The point is configure both scroll view and content's constraint with using contentLayoutGuide
Situation
- In Swift, you have some large content, larger than screen than you want to display like an article.
- You don't know the size of the content height before. And It may increase later.
- Instead of setting large enough and ambiguous size to the content before, you want to set exactly correct size so that you can avoid additional strange scroll.
Of course this can be solve by using tableView or collectionView. However, those view are complicated to use and sometimes you want to as simple as possible. For example, do you want to use tableView or collectionView to just display long article?
Short answer
I found a way to implement this. The solution is
- Set both scrollView and its content's constraint.
- Set the content area of scrollView with
contentLayoutGuide.
The final example will like this. The content size is determined after the view is loaded and set. Even if you increase the content, the scroll is automatically adjusted!
I created a sample project so you can easily look it.
Details
Configure the Scroll view
Firstly, configure scroll view.
- Main view: color is white
- Scroll view: color is gray and have margin 24 spaces from main view.
- Content view inside the scroll view: color is blue.
let scrollView = UIScrollView()
view.addSubview(scrollView)
scrollView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
scrollView.backgroundColor = .systemFill
let scrollViewMargin:CGFloat = 24
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
scrollView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.topAnchor, constant: scrollViewMargin),
scrollView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor, constant: scrollViewMargin),
scrollView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor, constant: -scrollViewMargin),
scrollView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.bottomAnchor, constant: -scrollViewMargin)
])

Configure the Content
Let's add a content which is vertically long. We can scroll vertically but not let scroll horizontally.
At first, we create a content with stack view and add to the scroll view. This doesn't have to be stack view but for the easy explanation, I selected it.
let dynamicSizeContent = UIStackView(arrangedSubviews: [])
scrollView.addSubview(dynamicSizeContent)
dynamicSizeContent.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
dynamicSizeContent.backgroundColor = .systemTeal
dynamicSizeContent.distribution = .fill
dynamicSizeContent.spacing = 16
dynamicSizeContent.axis = .vertical
Now let's set the constraint to this content. It is vital to set constraint of the content. Let's first set the width rules.
let contentMargin:CGFloat = 24
// Width with margin
dynamicSizeContent.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: scrollView.widthAnchor, constant: -2*contentMargin).isActive = true
// Optional
dynamicSizeContent.centerXAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: view.centerXAnchor
).isActive = true
What is this doing? The first half decides the width of content. The content width is same as scroll size but 24 spaces shorter both from left and right. This is kind a padding if you want to set.
The second half keeps the content to be center. This will center and fix the content. If the content is horizontally short enough, you don't need this.
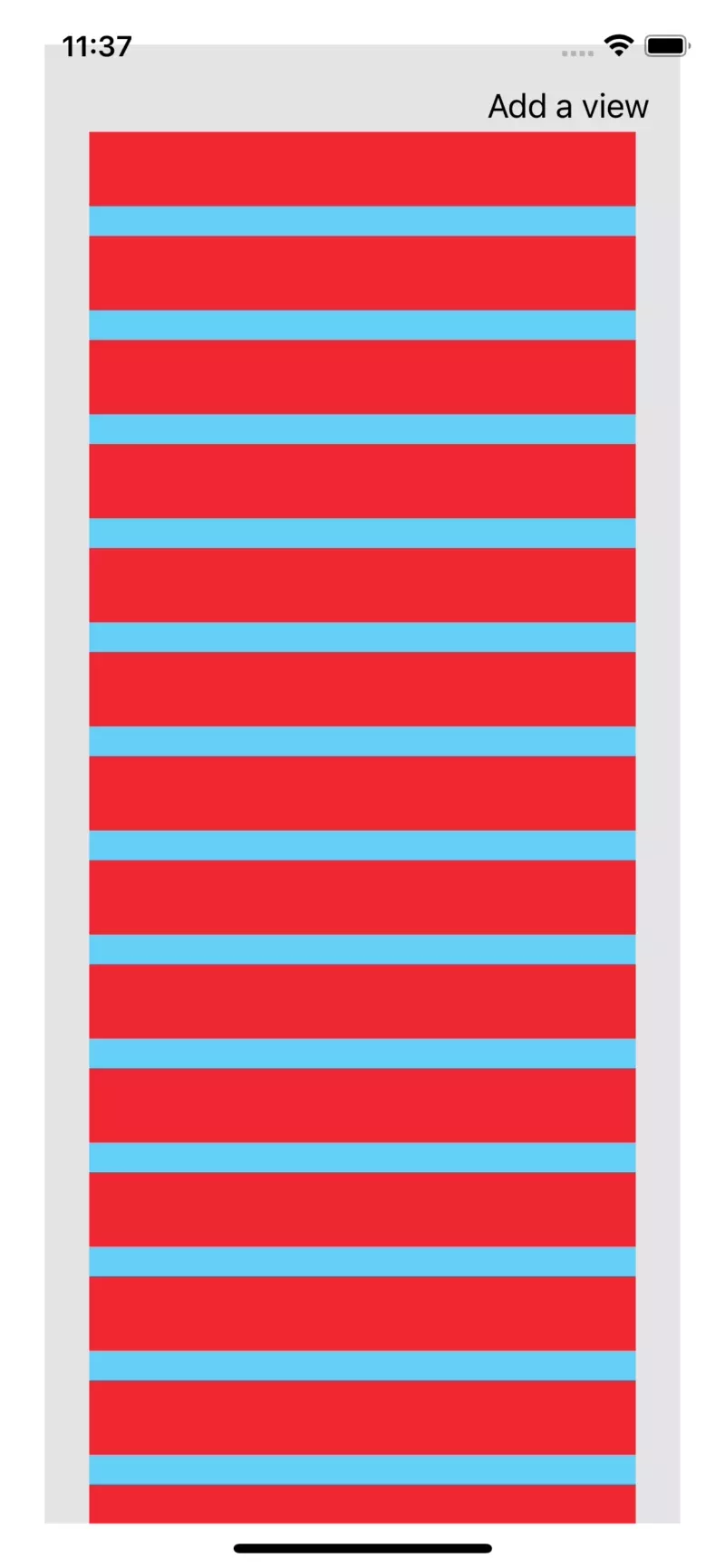
Dynamically increase content
I made an simulation to make the content dynamically increase. This is a function that append sub views (red ui view) into the content of scroll views.
private func addToDynamicContent() {
let uiv = UIView()
uiv.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 40).isActive = true
uiv.backgroundColor = .systemRed
dynamicSizeContent.addArrangedSubview(uiv)
}
And I call this in viewDidLoad() after configuring all views. This means the content changes after every view is configures.
for _ in 0..<40 {
addToDynamicContent()
}
I also created a UIButton which will execute above function when it's tapped. This simulates varying content after viewDidLoad() and viewDidApper().
@objc func buttonTapped() {
addToDynamicContent()
}
Right now the scroll view is not working. Even if you add come sub views and set constrains to them, it won't scroll. This is because we haven't configure any content area.
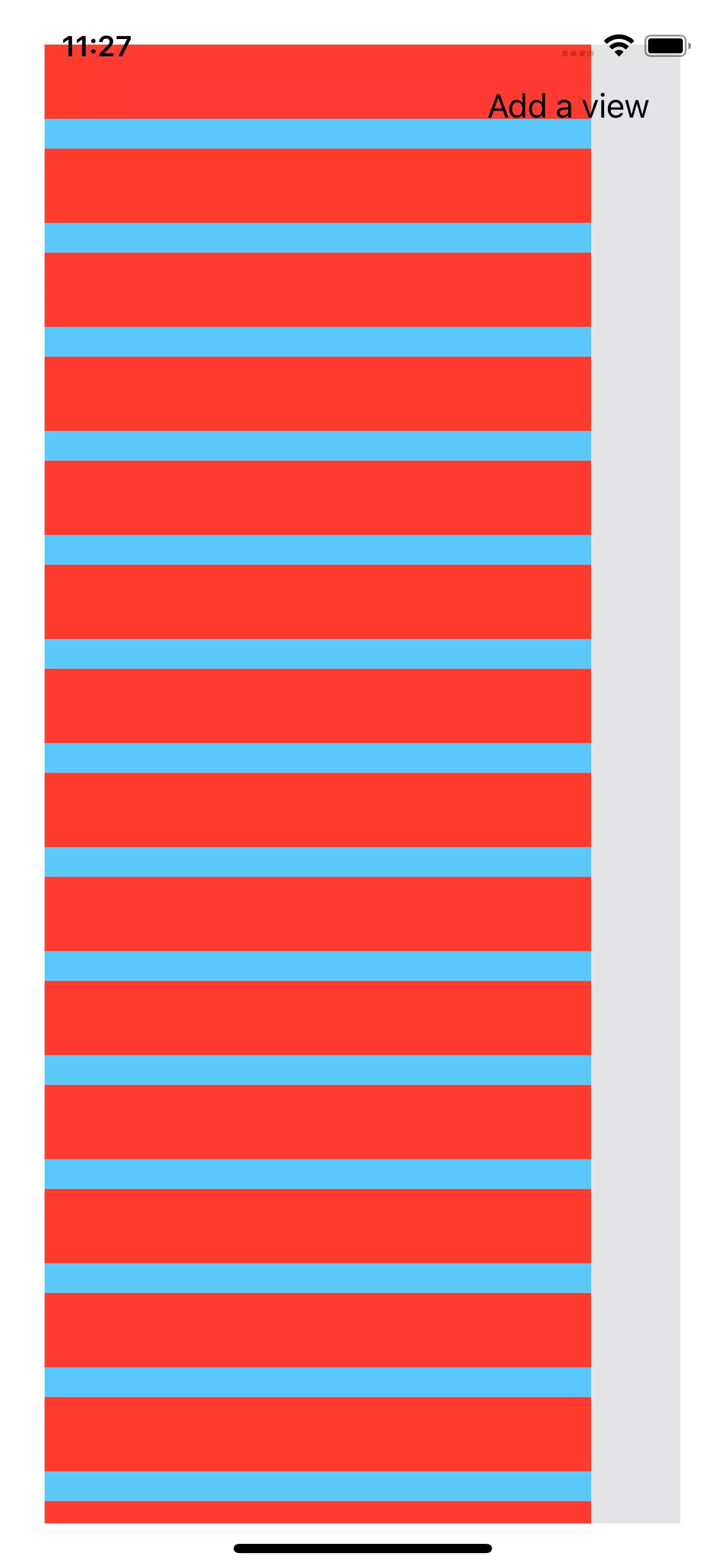
Configure the Content area
Now let's set the content area for scroll view.
let sa = scrollView.contentLayoutGuide
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
dynamicSizeContent.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: sa.topAnchor, constant: contentMargin),
dynamicSizeContent.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: sa.leadingAnchor, constant: contentMargin),
dynamicSizeContent.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: sa.trailingAnchor, constant: -contentMargin),
dynamicSizeContent.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: sa.bottomAnchor, constant: -contentMargin)
])
This is all! The key is contentLayoutGuide. By setting, the content area of scroll view will be automatically determined by the size of content view (dynamicSizeContent).
More simply way
Tired to prepare this? Don't worry! I prepared a custom subclass of UIStackView.
// contentView can be dynamic height.
var scrollView = DynamicHeightScrollView(
contentView: contentView,
padding: .init(top: 32, left: 32, bottom: 32, right: 32)
)

Conclusion
When content view inside the scroll view is very large, or you're not sure how large it'll be, setting content constraint by using contentLayoutGuide will easily make the scrolling better!
You can look further from this sample project.